








As you will be aware if you have already come across our blog, perforated metal mesh is a remarkably versatile material, finding applications across a multitude of industries, from architecture and engineering to design and manufacturing.
As a result of its unique ability to combine functionality with aesthetic appeal, it is a preferred choice for various applications, including but not limited to building facades, ventilation systems, and decorative panels. In order to fabricate perforated metal mesh, two sophisticated techniques are used: punching and laser cutting.
Depending on the project requirements and design specifications, each method offers its own advantages and capabilities. Punching involves mechanically creating holes in metal sheets, a traditional but highly efficient process. While laser cutting offers unparalleled precision and flexibility, it is a more modern approach. In this exploration, we will delve into the intricacies of these fabrication techniques, providing a comprehensive understanding that goes beyond the basics. By dissecting the processes behind perforated metal mesh we aim set the stage for an in-depth appreciation of this versatile material.
Let’s get into it…
Punching Technique
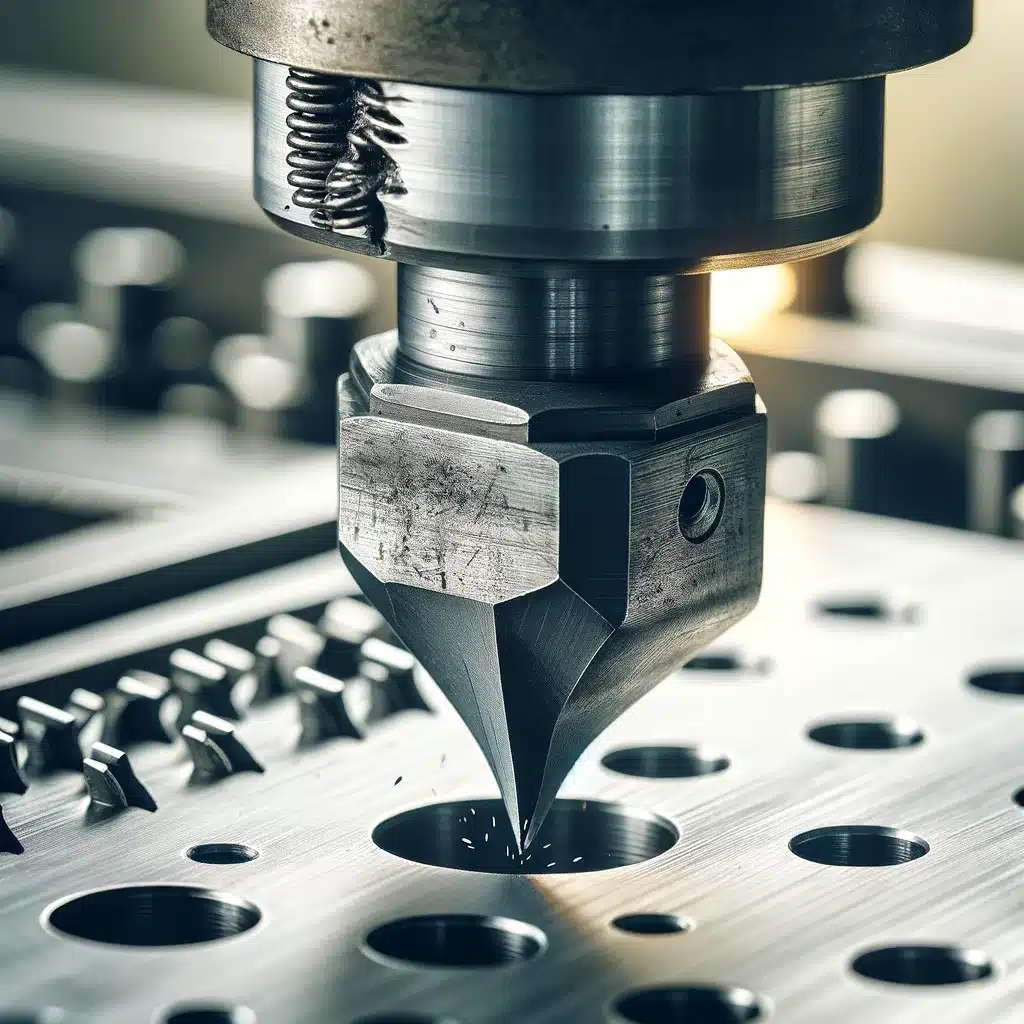
In mechanical punching, tools and machinery are used to exert force on metal sheets, effectively removing pieces of the material to create holes. Metal sheets are typically punched using a punch press, which drives a die into the desired hole shape. From simple round holes to complex geometric designs, the process can produce a wide range of perforation patterns.
Among the materials suitable for punching are aluminum, stainless steel, and mild steel. Material selection is largely based on the application’s specific requirements, such as strength, weight, and environmental resistance. Especially suitable for high-volume production runs, punching is highly regarded for its speed and efficiency.
The method, however, has some limitations. As a result of the physical stress exerted on the metal during punching, deformations can sometimes occur around the perforations. In addition, punching tools can limit the range of possible designs.
Laser Cutting Technique
In the fabrication of perforated metal mesh, laser cutting provides a high level of precision and versatility. A high-powered laser beam is focused onto the metal surface, vaporising the material in a precise and controlled manner. Mechanical punching would be difficult to achieve intricate patterns and fine details.
With the process, designers and engineers are able to work with a wide variety of materials and thicknesses. Especially for complex or delicate designs, laser cutting’s precision is essential.
By using laser cutting, you can create custom patterns and produce cleaner edges with minimal material deformation. For larger production runs, it can be more time-consuming and more expensive than punching. Laser cutting for perforated metal fabrication is also complicated by the need for specialised equipment and operations.
When comparing punching and laser cutting, it’s evident that the choice depends on specific project requirements, including precision, design complexity, production volume, and cost.
As manufacturers, we must understand the differences between punching and laser cutting when fabricating perforated metal mesh.
For high-volume projects, punching generally incurs lower operational costs than laser cutting. It is a cost-effective choice for standard patterns and designs because the initial setup and machinery are less expensive.
Another important factor is speed. Due to the ability to process multiple perforations simultaneously, punching offers a faster production rate. As a result, it is ideal for projects requiring a quick turnaround. While laser cutting is precise, it is slower, meticulously cutting one hole at a time. Laser cutting, however, is capable of producing intricate patterns and shapes that punching cannot.
The amount of material wasted varies between the two techniques. As punching physically removes sections of the metal, it can result in more material waste. With a focused beam, laser cutting minimises excess waste around the cut areas, making it more resource-efficient.
The right method depends on the specific requirements of the project. For large orders requiring rapid completion and where design complexity is minimal, punching is the best option. In contrast, laser cutting stands out for projects requiring precision, intricate details, and minimal waste despite its higher cost and slower speed.
Metal mesh can be fabricated from a variety of materials, each offering unique benefits. Architectural applications and outdoor settings benefit from aluminium’s lightweight nature and corrosion resistance. Stainless steel, known for its strength and durability, is ideal for industrial environments and areas requiring stringent hygiene standards, such as food processing plants. In decorative applications and settings where its patina can be appreciated over time, copper offers an aesthetic appeal and natural antimicrobial properties.
A mesh’s material selection has a significant impact on factors such as weight, strength, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Stainless steel and aluminium are preferred in architectural and industrial applications for their durability and low maintenance, while copper is preferred in artistic and interior design applications for its natural beauty.
Its versatility is further enhanced by the variety of finishes available for perforated metal mesh. Powder coating can be applied in various colours to match design schemes, enhance corrosion resistance, and improve UV stability. Anodising provides a hard, protective layer that enhances aluminium’s natural lustre. For steel mesh, galvanisation provides robust protection against rust and degradation, extending its lifespan.
Ultimately, perforated metal mesh fabrication materials and finishes depend on the specific application requirements, environmental conditions, and aesthetic goals. Various combinations of materials and finishes provide distinct properties that can enhance durability, appearance, and performance.

Perforated metal mesh has a wide range of applications, each leveraging its unique properties to satisfy a specific functional or aesthetic need. It is used for building facades, offering not only a modern look but also benefits such as sunlight modulation and natural ventilation, enhancing a building’s energy efficiency.
Perforated metal is used in industrial manufacturing to make filtering systems, machinery guards, and noise control panels, demonstrating its durability and strength. Perforated metal is used in radiator grilles and exhaust components in the automotive industry because of its heat resistance and airflow abilities.
Perforated metal is used in artistic installations to create immersive experiences. A perforated metal installation at the High Museum of Art in Atlanta illustrates how the material can transcend its industrial origins while embodying artistry and elegance.
In urban landscaping, perforated metal is used to enhance public spaces by integrating benches, lighting fixtures, and pathway screens. In addition to contributing to urban areas’ visual appeal, these installations address practical needs such as lighting and seating.
Metal mesh with perforations has a number of advantages that make it a popular material for a variety of projects. As it transforms light and space, it creates patterns and textures that add depth and interest to any design. In architectural applications, it is crucial for creating comfortable and energy-efficient environments as it provides excellent ventilation and light diffusion.
At the point of manufacuture, perforated metal can be customised in a variety of patterns, hole sizes, and materials to meet specific design and functional requirements. This is not the case with woven wire mesh for example.
The use of perforated metal in building contributes to sustainable practices from an environmental perspective. Through natural lighting and air flow, it reduces the need for artificial lighting and air conditioning, thus enhancing a project’s energy efficiency. The eco-friendliness of perforated metal mesh, combined with the recyclability of materials like aluminum and steel, underscores its importance to modern design and construction.
The perforated metal mesh landscape is constantly evolving, with current trends and innovations pushing the boundaries of design and application. The increasing use of digital fabrication techniques, such as 3D printing and advanced laser cutting, has opened up new possibilities for customisation and complexity in patterns that were once unachievable. Architects and designers can now create more intricate and bespoke installations thanks to these advancements in precision and flexibility.
Furthermore, coatings and finishes have been developed to enhance both the aesthetic qualities and the functional performance of perforated metal. Architects are exploring smart coatings that respond to environmental conditions, such as temperature and sunlight, to save energy.
Additionally, alloy compositions have been experimented with to produce perforated metals with improved strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, enabling them to be used in harsher environments.
With its aesthetic appeal as well as functional benefits such as light diffusion, ventilation, and energy efficiency, perforated metal mesh is an excellent choice for a wide range of projects.
With its traditional punching technique and its precision laser cutting technique, along with innovations in material treatments, this material is ever-evolving. By offering both visually striking and environmentally conscious solutions, perforated metal mesh remains at the forefront of design and construction trends.
Our conclusion encourages readers to explore the potential of perforated metal mesh for their upcoming projects. It is possible to achieve specific aesthetic objectives or to address practical concerns with the array of patterns, materials, and finishes available today. Visit our extensive range of perforated metal products and services, where our team of experts can provide advice and support, ensuring you select the best solution for your unique needs.
As always, thank you for checking out our blog. We hope that this helps you with your project. We try to launch a couple of new guides every week. Eventually we will have covered everything there is to cover about mesh.
You may be interested in our blog that explores hexagonal vs square hole perforated metal mesh.
Our goal for our blogs and help guides is to answer as many questions as possible to help to explain the possibilities of mesh to our customers.