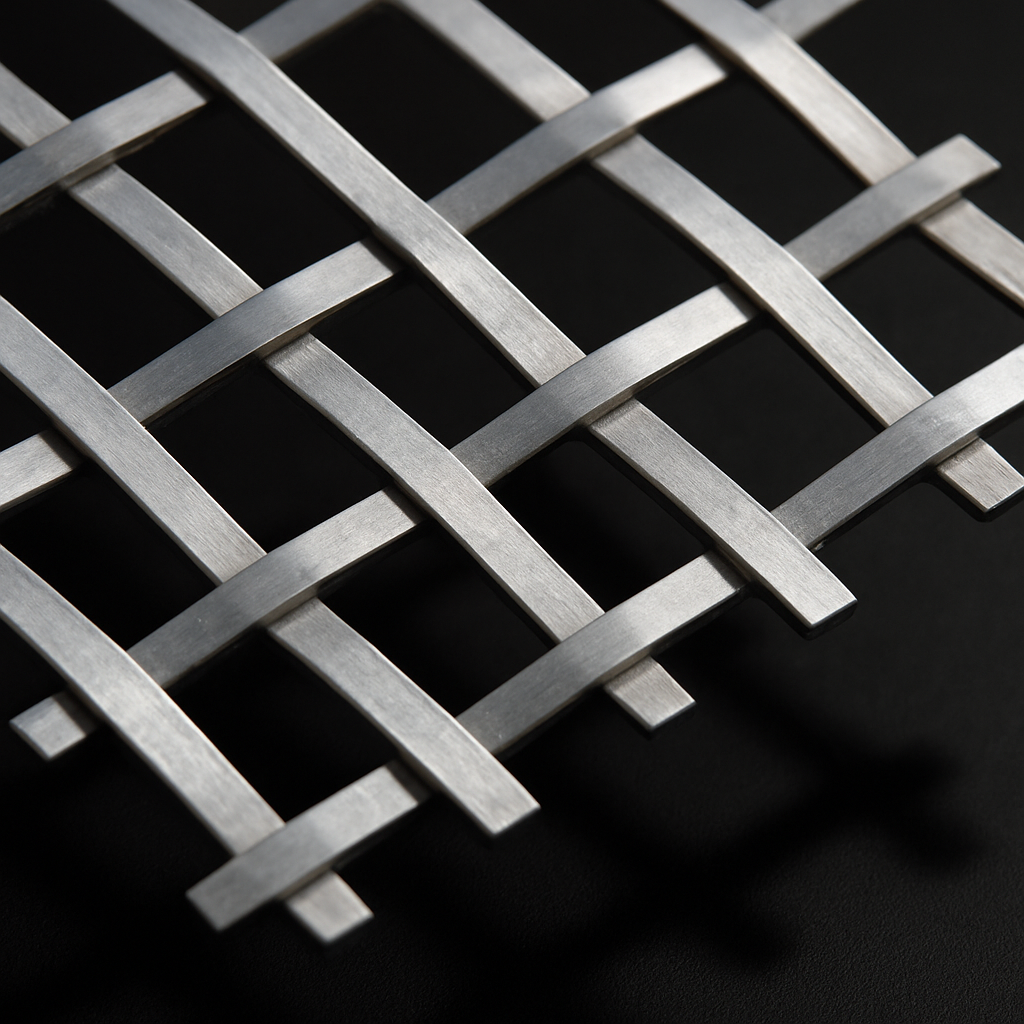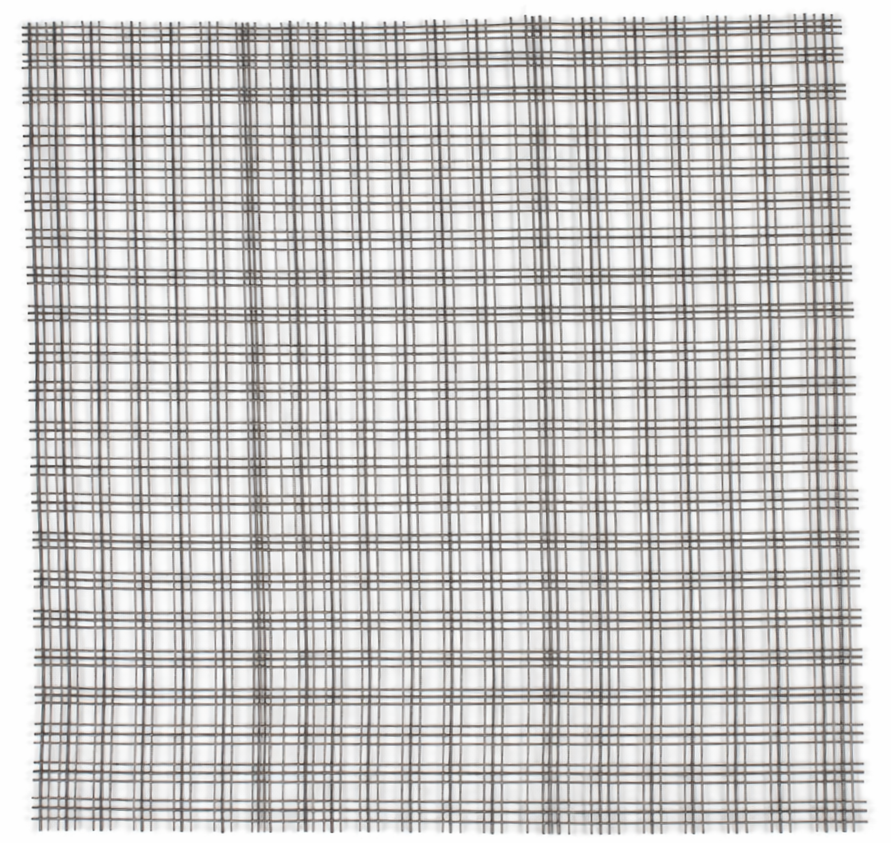









Woven wire mesh is a the type of wire mesh that we are most associated wire. It is a type of fabric, or hardware cloth, made from metal wires woven together in a grid pattern.
Woven wire mesh is used for a variety of purposes, such as filtering, sieving, and shielding. It’s also used for decorative purposes and to make baskets.
But we are constantly being asked about how to work out the sizes of our mesh. This short article aims to answer any question that you may have.
Let’s get into it….
Mesh size is determined by counting the number of openings in one linear inch of mesh. This measurement is called mesh count or mesh number.
The higher the mesh count, the smaller the opening size. For example, #10 mesh has ten openings per inch in each direction and can be described as “ten by ten” or “10 × 10” mesh. We refer to woven mesh on this site as ‘LPI’. This means Lines Per Inch.
If there are 10 holes per linear inch, then there will 10 wires per linear inch. Or, more commonly, 10 lines per linear inch. Hence ‘LPI’.
The term “aperture size” refers to the space between two adjacent wires in a given section of wire cloth or mesh.
Apertures can be measured using either microns (μm) or millimetres (mm).
A micron is a unit of measurement used to express the size of particles, fibres, or other microscopic objects. It is often used with woven wire mesh because this can be woven into incredible fine cloth like structures.
It is also known as a micrometre and is abbreviated as µm.
One micron is equal to one millionth of a meter (1/1,000,000 m) or 0.001 millimetres (mm). Microns are commonly used in fields such as microscopy, biology, and engineering to measure the size of small objects, such as cells, bacteria, and particles.
Our finest mesh product has 500 holes per inch, and as such an extremely small 26 micron (µm). To put this into context, the size of a human red blood cell is typically around 7 microns, and a strand of human hair is roughly 50-100 microns in diameter. It is ridiculously fine.
Mesh this fine would be used to filter fine powder, paints and pigments. It is also used to remove impurities from fine chemicals to ensure that the final product is pure.
Yes there is. To calculate the hole size of a woven mesh, you can use the following simple formula:
Hole Size = (Wire Thickness / (Holes Per Inch + Wire Thickness)) x 25.4
Where:
The formula above assumes that the mesh is woven in a square pattern (i.e., the wires running in both the x and y directions are of the same diameter).
The factor of 25.4 is used to convert the result from units of inches (which the formula assumes for consistency with the wire thickness) to units of millimetres (which are more commonly used for expressing mesh sizes).
So, for example, if you have a mesh with a wire thickness of 0.5mm and 20 holes per inch, the hole size would be:
Hole Size = (0.5 / (20 + 0.5)) x 25.4 = 1.13 mm
Therefore, the hole size of the mesh would be approximately 1.13 mm.
This mesh is one of the strongest and most popular that we offer.
It has 4 holes per linear inch. Which means that it has 4 wires per inch, or 4 LPI.
The wires are 1.2mm thick.
This leaves a square hole of 5.1mm.
The title of this mesh product is – ‘5.1MM HOLE HEAVY DUTY WIRE MESH – 304 STAINLESS STEEL – 1.2MM WIRE – 4 LPI‘

As always, thank you for checking out our blog. We hope that this helps you with your project. We try to launch a couple of new guides every week. Eventually we will have covered everything there is to cover about mesh.
You may be interested in our blog that explores hardware cloth.
Our goal for our blogs and help guides is to answer as many questions as possible to help to explain the possibilities of mesh to our customers.